Table of Contents
Hedera Hashgraph is one of the “hot” pieces among the new cryptocurrencies. In recent months, the coin has performed very well in terms of price. Therefore, we look in detail at what Hedera Hashgraph is, why it has such value and what risks are associated with this currency.
Hashgraph is not a blockchain
The first, significant difference from most cryptocurrencies is that Heder’s network does not have a blockchain structure. Instead of blockchain, there is a so-called Hashgraph, which has a different architecture and allows different, technological solutions.

The network architecture is one of the so-called DAGs (Directed Acyclic Graph – similar system has IOTA, NANO, or the newly emerging Fantom network). This allows computers in the network to communicate directly with each other, and there is consensus, allowing for increase speed of transaction and umber of them. Blockchain, on the other hand, is limited by individual blocks and their sizes.
Consensus (network state matches) is accomplished in the network using two tools. The first is virtual voting, where each node votes on conflicting transactions and selects only one. The second tool is Gossip to Gossip protocol. This is basically a series of rules according to which information is spread over the network. Thanks to Gossip to Gossip technology, the network is very fast. Each node in the network sends network status information to everyone else, and after some time there is agreement on exactly what the network history looks like.
DAG architecture is a promising technology, but it has one crucial catch. That is centralization. Like IOTA, the Hedery network relies on a limited number of consensus participants.
Model of management and verification of transactions
The Hashgraph is, as has been said, DAG. This also has implications for the architecture of the network itself. While it is faster and according to optimistic estimates, it could handle up to 10,000 transactions per second (VISA around 2000 TPS), but it is primarily due to the limited number of network validators. There are two main control bodies in the Hedera network.
In the case of transaction verification, they are the nodes themselves. While the Hedera team promises greater decentralization, at the beginning of the network only 39 selected companies will participate in the consensus. They will operate the individual nodes. In the future it is planned to involve more independent entities in network health verification, but this is the music of the future.
The 39 companies will form a Governing Board (similar to the Pound Association in the currency project created by Facebook). The Council will decide on key issues in the network. This means that the Council will decide how the whole network will evolve. For example, hardforks will not be possible in the Hedery network. There will be a single system which will be decided by the Council.
Individual nodes thus have the right to vote on consensus and to verify that they all respect the rules of the network, but only the Council will decide on the actual development of the network. The seat in the Council is for 2 years and at most one company can hold such a seat for 4 years at a time. This is to ensure sufficient decentralization of the network.
Why Hedera succeeds
Hedera has one very concrete and huge advantage. This is the Governing Board, which is now formed from large companies. Unfortunately, for cryptocurrency is a disagreeable centralization, however, for large, commercial entities, just such a version of the digital, financial system may be beneficial.

Most important, however, are the names that Hedera has already received in the Council. So far, 11 out of 39 seats are occupied. The biggest names are definitely Google, Boeing, Deutsche Telecom, FIS and IBM.
The architecture and management of the Hedera system also enables one of the critical things for the medium-term outlook, namely the ability to comply with legislation and regulations. Being managed by large corporations, the entire system will have ample capacity and capacity to make Hedera compatible with national regulations.
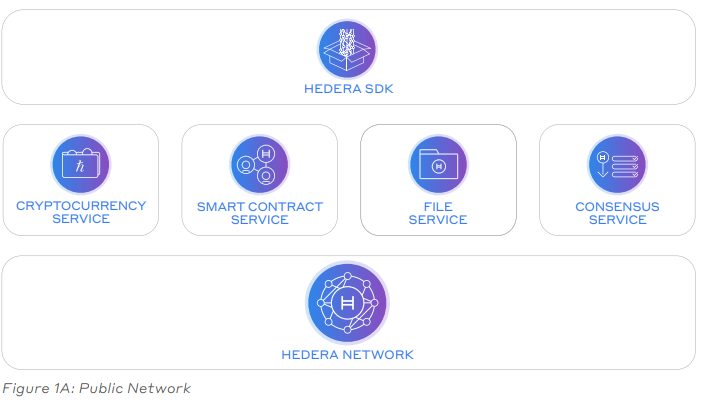
Hedera offers standard services that are common to smart contract platforms such as ETH, NEO, Tezos and more. In addition, it provides an integrated service in the form of a “decentralized” data store. But there are doubts about where the repository is really decentralized, because the platform itself is now heavily centralized.
Why Hedera fails
Hedera has several very problematic parts. First of all, it is the decentralization of the network and the huge influence of the management structure. Ordinary users, as well as node operators or developers, have virtually no say in the network, and everything important is decided by the Council, including the monetary policy of the system. This means, for example, that the total volume of coins in the net may change.
HBAR is a native coin network. Only the miniature fraction is circulating. 6.3% of the total amount of HBAR coins is in circulation. The total number of coins (but may change at the Council’s discretion) is 50,000,000,000 and is now in circulation of 3.3 billion HBAR.
Another problem is the uncertainty in the use of the DAG model. For the time being, there is no long-term, decentralized DAG. This technology does not have proven functionality, as is the case with blockchain technology. The biggest DAG is still IOTA (at least according to market capitalization) and it still has many problems and is actually centralized.
Summary
Hedera Hashgraph is a project to be digital and financial for everyone. For the time being, however, it seems that the target group is primarily corporations. And that’s okay. Corporations are likely to find sufficient use for a network that they will jointly control. There are risks for the average user, however, when omnipotent Councils and the lack of decentralization can be feared.
HBAR has a disastrous, token economy where most of the coins are held by Swirlds, which is behind the development of the Heder network. To operate the node it is necessary to stake the HBAR coin. However, at the outset of the network, the operation of the network is provided by the Council and primarily by Swirlds, which is the only firm in the Council, which has the only fixed place.
The Hedera network is remarkably reminiscent of Ripple and XRP, where one company controls most of the network through token ownership. It is expected that Swirlds will gradually sell HBAR coins similarly to Ripple.
[coinlib-widget type=1 coinid=1511303 prefcoinid=1505 dark=0]
- Russia to Slap a 15% Tax on Crypto Gains – The Bear Wants Its Share - November 20, 2024
- 70% of Airdrop Tokens Are Profitless—Here’s Why Your Freebies Might Be Worthless - November 19, 2024
- The Most Important Cryptocurrency News of November 14, 2024 - November 15, 2024























