Table of Contents
Recent updates on US inflation paint a complex picture. However, despite ongoing economic concerns, there is a notable shift in some key metrics.
The latest news and developments on inflation in the USA
US consumer sentiment fell for the fourth consecutive month in November. This decline reflects broader concerns about the economy, particularly as households face higher inflation rates in the medium term.
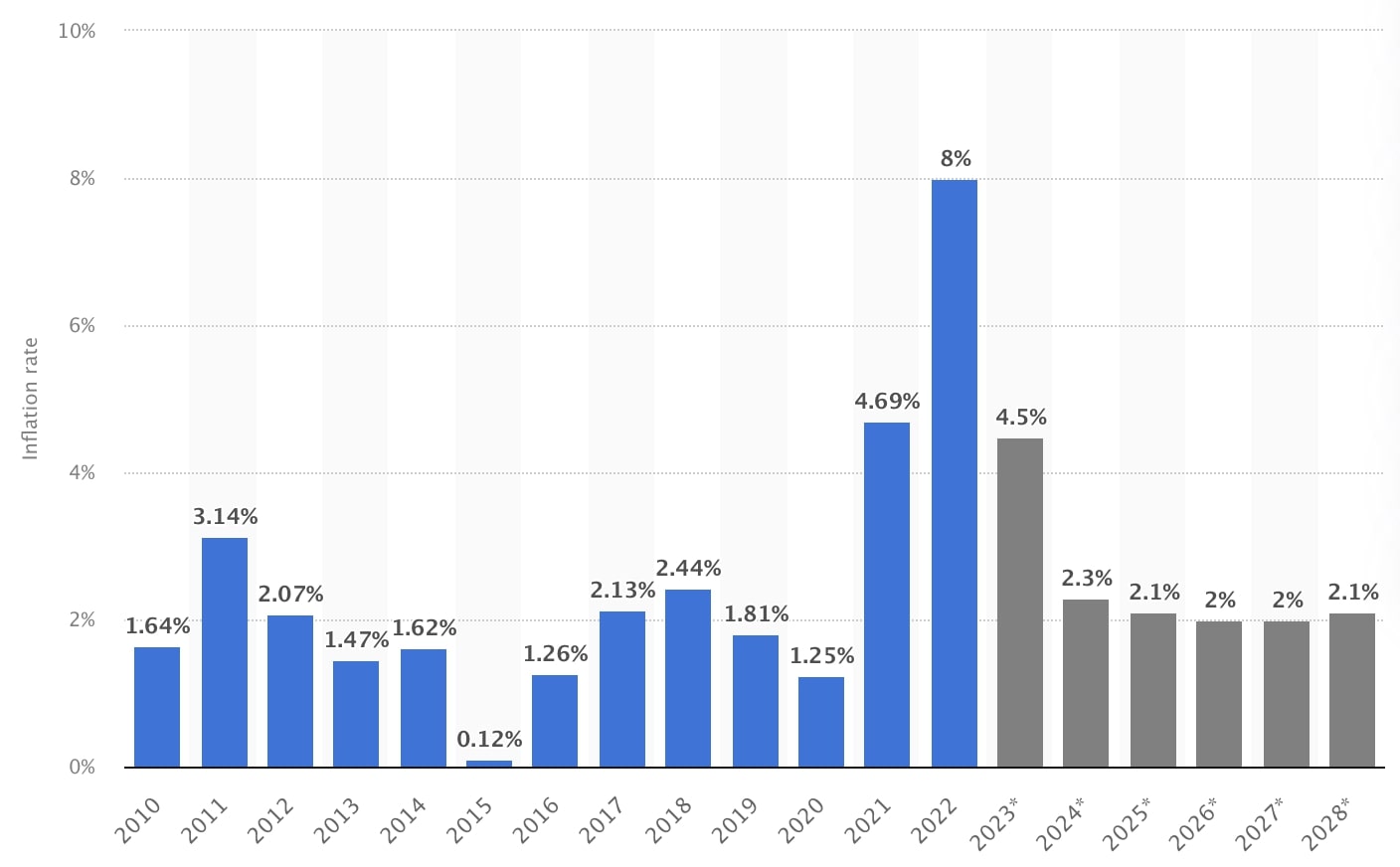
The actual annual inflation rate in the US was at 3.2% in the 12 months ending October 2023 – a decrease compared to 3.7% in the previous year.
What factors are currently influencing inflation rates?
There was no increase in US consumer prices in October, marking the smallest increase in underlying inflation in two years. This relative stability is due in part to lower energy costs (including heating oil, gasoline and gas), which have eased pressure on overall consumer spending.
Food, new car prices and housing costs also increased less than expected, while prices for used trucks and cars fell slightly.
On the other hand, there was an increase in prices for transport, clothing and medical goods. Overall, the core consumer price index was 4% year-on-year in October and 0.2% month-on-month. Both figures were lower than expected.
Even though inflation has slowed recently, American households are expecting growth, forecasting a rise to 4.5% next year. This estimate is higher than the 4.2% in October and 3.2% in September, according to the University of Michigan Consumer Survey emerges.
Global conflicts and trade tensions
The conflict between Israel and Hamas raises concerns about potentially broader tensions in the Middle East that could affect prices for energy and other raw materials. US sanctions against Iran and possible retaliatory measures, including threats against the Strait of Hormuz, could further exacerbate these problems.
In addition, inflationary pressures are compounded by ongoing tensions between the US and China over semiconductor production. The US export ban on certain chips to China, including those from Nvidia and Intel, leading to further supply chain disruptions.
This mixed scenario underscores the challenges the US faces in balancing inflationary pressures, consumer expectations and market realities. While the last few months have brought some relief, the public remains concerned about possible cost increases in the near future.
US Inflation Rate Forecast for 2024 and Beyond
According to Statista, the forecast inflation rate in the USA could fall from the current 3.2% to 2.3% next year. It is expected to fall even further to 2.1% in 2025 and to 2% in 2026 and 2027.
However, in 2028 it could increase slightly again and reach 2.1%.
Syed Mohammed Osama Rizvi, energy and macroeconomics analyst at Primary Vision Network, told:
“Predicting the US inflation rate is a delicate matter as it involves several aspects. First of all, we need to consider the likelihood of interest rate hikes. Many observers believe there will be no further increases and by June 2024 we could see the current monetary tightening lifted.“
Rizvi added: “I believe that given the unresolved geopolitical events, the likelihood of further rise in inflation remains high. The chances of further interest rate increases therefore still exist. Additionally, the job market and consumer spending remain strong.“
“Therefore, I don’t think inflation will fall much next year. If there is a global recession, with major economies like the US experiencing a downturn by the second quarter of next year, inflation could ease somewhat weaken. However, this will come at a price.“
Piero Cingaro, journalist at the financial intelligence service Benzinga, said that “The Federal Reserve’s latest macroeconomic forecasts indicate a gradual decline in inflation rates. These forecasts assume inflation will average 2.5% in 2024. After that, it could fall to 2.2% in 2025 and move closer to the Fed’s 2% target by 2026“.
“The latest global economic outlook from the IMF assumes a similarly favorable development in inflation. In 2024 it is expected to be 2.3% and fall further to 2.1% by 2028. The market consensus appears to agree with these US inflation forecasts. Current market estimates of forward-looking inflation rates, known as breakeven inflation rates, suggest an average inflation rate of 2.2% to 2.25% over the next five to 10 years. These rates are consistent with pre-pandemic averages.“
Cingari also noted that in the meantime “a divergent view is being observed among US consumers“.
“The latest consumer survey data from the University of Michigan shows that concerns about inflation has increased. Consumer inflation expectations for next year rose to 4.4%, the highest since April. U.S. consumers’ inflation expectations for the next five years have also climbed to 3.2%, a high not seen since March 2011.“
Deloitte divides its inflation forecast for the USA into four possible scenarios for the near future. These include a soft landing, a bumpy landing, a hard landing and a crash landing.
- Soft landing
In the event of a soft landing, the inflation rate in the US could return to the Fed’s 2% target. However, this would happen without triggering a recession.
This is the best-case scenario in which economic conditions essentially return to what they were before the pandemic. However, given the current geopolitical situation, this is highly unlikely.
- Bumpy landing
If there is a bumpy landing, inflation may weaken slightly from the current 3.2%. However, it still doesn’t quite reach the 2% target.
This could be due to problems in the labor market. However, growth is still there, albeit a little slow.
- Hard landing
A hard landing could be caused by the Federal Reserve’s overzealous monetary tightening policy. This could cause inflation to fall below the 2% target.
This development could also be due to other factors, such as: Supply chain interruptions can be accelerated. In addition, consumer demand could decline more quickly than previously assumed.
- Crash landing
In the event of a crash landing, the inflation rate in the USA will not go down. It remains uncomfortably high due to a potential wage-price spiral and constant supply shocks.
Morningstar on the other hand, expected inflation in the USA between 2024 and 2027 is around 1.8%. This is primarily due to supply disruptions easing somewhat.
Prices for food, durable goods and energy are also expected to fall dramatically in the next few years. If this is the case, inflation will be below the US Federal Reserve’s target, which can also weaken the economy.
The US Federal Reserve has indicated that further tightening of monetary policy will have a negative impact on both households and the economy. Therefore, it says it will pay attention to additional economic data. This includes, in particular, labor market reports, financial and international developments and inflation reports. However, the Fed has reassured the public that the US banking system is resilient.
More about US inflation
What is inflation?
Inflation is the sustained increase in the prices of goods and services over time. It is usually measured quarterly or annually. This phenomenon can have various causes, e.g. increased money supply, increased demand or external geopolitical events.
In particular, the escalating costs of essential goods such as food, raw materials and energy can trigger inflation. These goods are essential to the production of numerous other products, leading to widespread price increases throughout the economy.
In order to get inflation under control, central banks often pursue more restrictive monetary policies, which results in higher interest rates. They can also alter their balance sheets and adjust the money supply as a measure to combat inflation.
The history of the inflation rate in the USA
From 1960 to 2022, U.S. inflation remained generally low and well controlled, although there were occasional spikes.
There were significant increases in 1970 (5.84%), 1974 (11.05%) and 1980 (13.55%), which was probably due to the oil crisis of the 1970s.
This was exacerbated by escalating tensions between the US and the Middle East, which affected prices for energy and other goods. However, since 2020, inflation in the USA has risen sharply and continuously. In November 2021 it reached around 6.8%. A 40-year high of 9.1% was recorded in June 2022.
This increase is primarily due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic as well as escalating energy prices due to the Russia-Ukraine conflict and significant supply chain disruptions. In response, the Federal Reserve has made a series of aggressive interest rate hikes in recent months.
Other central banks, including the Bank of England and the European Central Bank, have also taken similar measures, in part because of the spillover effect of US inflation on the economies of the UK and EU. The Fed has mostly raised interest rates in 0.50% increments, occasionally opting for 0.25%.
However, in recent months it has kept interest rates at 5.25% to 5.50% to allow time to analyze incoming economic data and determine future actions.
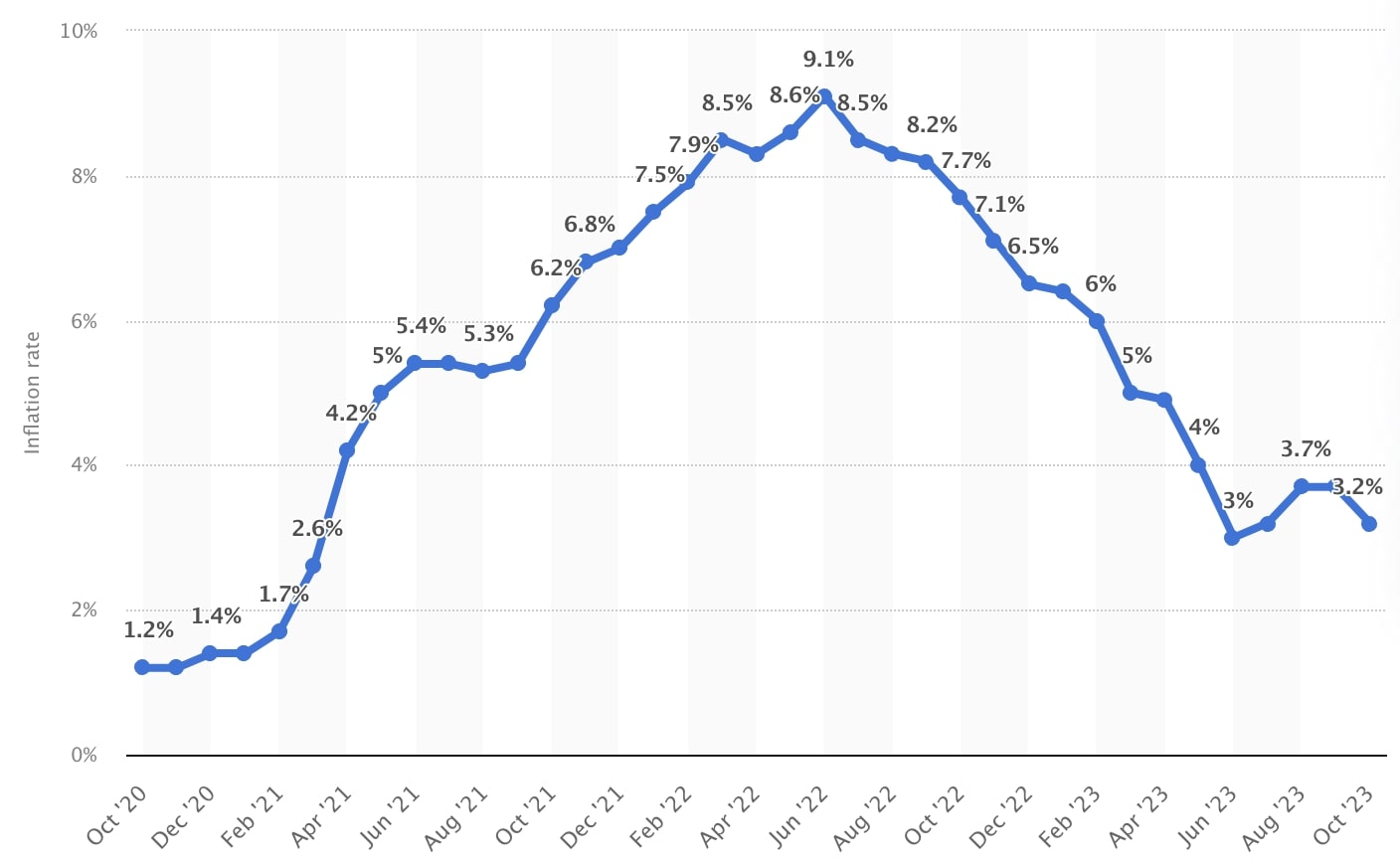
This pause reflects both a faster-than-expected decline in inflation and the U.S. economy’s growing proximity to recession, requiring a more cautious approach.
- Why Online Advertisers Should Request Website Traffic Data from Google Analytics Instead of Using SEO Tools Like MOZ or Ahrefs? - March 24, 2025
- North Carolina’s Bold Move: State Bill Proposes Investing 10% of Public Funds in Bitcoin - March 22, 2025
- Justin Sun Stakes $100 Million in Ethereum on Lido – What Does It Mean for the Market? - March 19, 2025

























