Vitalik Buterin, the co-founder of Ethereum, has introduced a conceptual architecture called anchored zero-knowledge Ethereum Virtual Machine (ZK-EVM) to improve the efficiency of the main chain.
According to Buterin’s last blog, this proposal aims at the anchored ZK-EVM aims to integrate advanced cryptographic techniques directly into the Ethereum main chain. This is intended to create a secure and efficient verification process for ETH transactions. In particular, the operation of Layer 2 applications should be improved and optimized.
A post on benefits and challenges of enshrined ZK-EVMs at layer 1:https://t.co/bRTKdtaFRL
There's different options and the tradeoffs get complex!
— vitalik.eth (@VitalikButerin) December 13, 2023
Anchored ZK-EVM on Layer-1
The core idea of an anchored ZK-EVM is to provide a native, in-protocol system for verifying Ethereum blocks with zero-knowledge proofs. This system aims to reduce dependence on external code bases and minimize the risks associated with errors in these external systems.
“This situation is suboptimal because these projects replicate functionality that already exists in the Ethereum protocol,” explains Buterin. The anchored ZK-EVM would essentially perform similar functions to current Layer-1 Ethereum blocks, but with improved security and efficiency. “The most important feature, in addition to the basic guarantees of correct functionality and security, is speed.
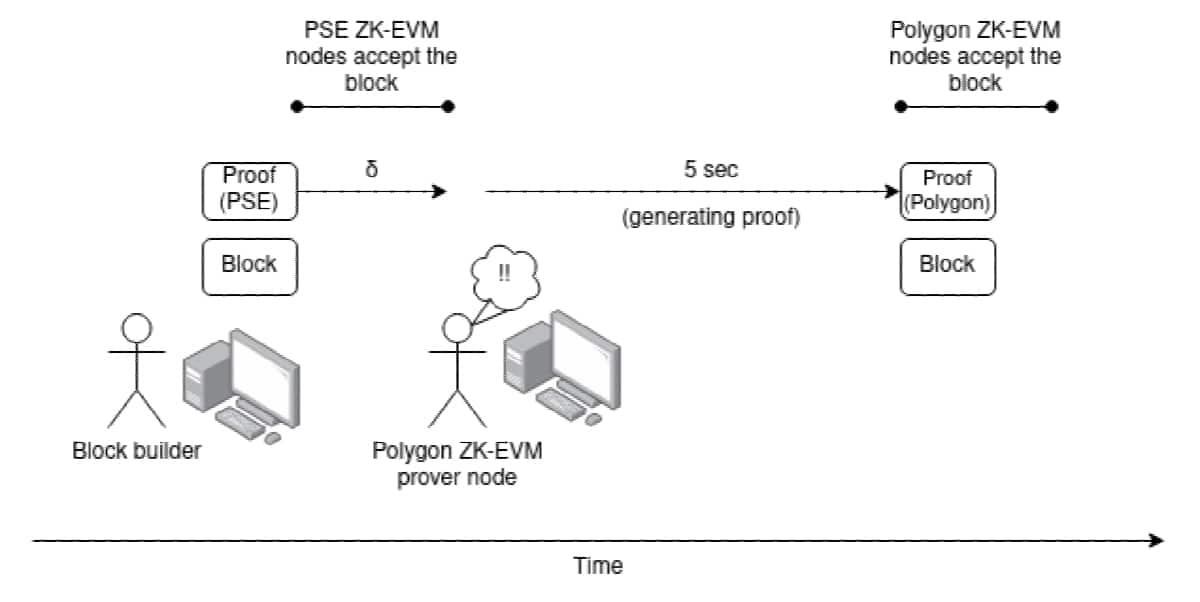
One of the most important aspects of this proposal is its compatibility with Ethereum’s multi-client philosophy. Buterin emphasized the importance of supporting different clients with different proof systems.
“Compatibility with Ethereum’s multi-client philosophy means we want to avoid imposing a single proof system and instead allow different clients to use different proof systems,” Buterin said.
Buterin also talks about the importance of ensuring the availability and verifiability of data in this system. He argues that any execution audited by the ZK-EVM must guarantee that the underlying data is accessible for review in the event of problems. This transparency is critical to maintaining trust and reliability on the network.
Ethereum: Important terms and concepts
To better understand the context of the anchored zero-knowledge ETH Virtual Machine, it is important to clarify some key terms and concepts:
Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZK Proofs): These are cryptographic methods that allow one party to prove to another that a statement is true, without any information about the validity of the statement itself to reveal. In the context of the Blockchain, ZK proofs enable transactions to be verified while maintaining privacy and reducing the amount of data that needs to be processed and stored.
Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM): The EVM works as a decentralized, global computer in which all ETH accounts and smart contracts exist and interact. Every transaction or smart contract executed on Ethereum is settled through the EVM, which acts as the central execution point for all network activity.
Layer 2 Solutions: These are technologies that are placed on top of a blockchain (known as Layer 1) to improve its scalability and efficiency. Layer 2 solutions, such as rollups or state channels, process transactions off the main chain but still derive their security from the underlying Layer 1 blockchain.
Crypto exchanges with the lowest fees 2023
- Well-known crypto analyst is ‘turbo bullish’ on FLOKI - January 8, 2025
- Bitcoin price drops 5,000 USD: What happened? - January 8, 2025
- Publicly traded company CleanSpark raises 9,952 Bitcoin, surpassing Tesla - January 7, 2025
























