Table of Contents
In the area of cryptocurrencies, there are growing concerns about the environmental impact of using blockchain. But a new solution based on Layer 2 technology could change everything.
While the decentralization of cryptocurrencies offers numerous advantages, it is often associated with increased energy consumption. But what if there was a way to maintain the decentralization and security of the blockchain while reducing the carbon footprint?
Below we will take a closer look at the L2 solutions and provide a holistic understanding of their impact on the environment.
Combining scalability and efficiency: how do layer 2 solutions work?
Ethereum, a leading blockchain platform, processes 500,000 transactions per day. For comparison: At Visas it’s 150 million. However, such a high rate can lead to network congestion and high fees.
Here come layer 2 solutions like polygon and others who want to address the scalability issue by offloading some of the workload from the mainnet (Layer 1).
3 types of Layer 2 solutions
- State Channels: Two-way communication channels that increase transaction speed, e.g. B. that Lightning Network from Bitcoin.
- Zero Knowledge Rollups: Using cryptographic tokens known as zk-SNARKs to consolidate transactions off the main blockchain to reduce fees, e.g. B. Polygon Hermez.
- Optimistic Rollups: Relying on fraud evidence and penalizing fraudulent transactions, e.g. B. arbitration.
These methods increase transaction rates from 16 transactions/second at layer 1 to 10,000 transactions/second at layer 2.
Crypto and “dirty” energy
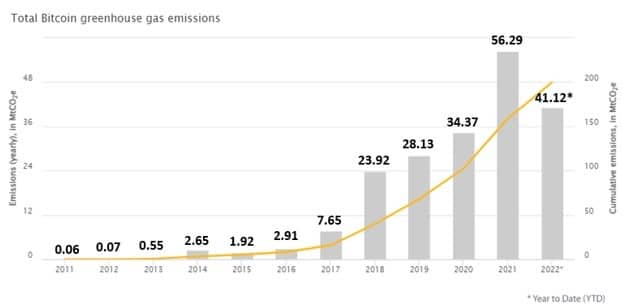
The environmental challenges of cryptocurrencies lie in their Proof-of-Work (PoW) technology. Alone Bitcoin is responsible for around 199.65 million tonnes of CO2 equivalent since its launch.
The energy-intensive nature of mining and the rapid increase in hash rate contribute to this problem. However, the decline in mining profitability and the development of energy-efficient hardware have led to a reduction in emissions.
The environmental concerns surrounding cryptocurrencies primarily relate to the energy consumption required to validate transactions.
In this process, known as mining, complex mathematical tasks are solved, which requires considerable computing power.
In traditional proof-of-work systems like Bitcoin this has led to an exploding demand for electricity, comparable to the consumption of entire countries.
Ethereum has recognized the problem and with Ethereum 2.0 Paved the way for a greener model by introducing a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism.
This paradigm shift aims to significantly reduce energy consumption and adapt the network to sustainability requirements – a crucial step in addressing the impact of cryptocurrencies on the climate.
Blockchain Layer 2 Solutions: A Sustainable Transition?
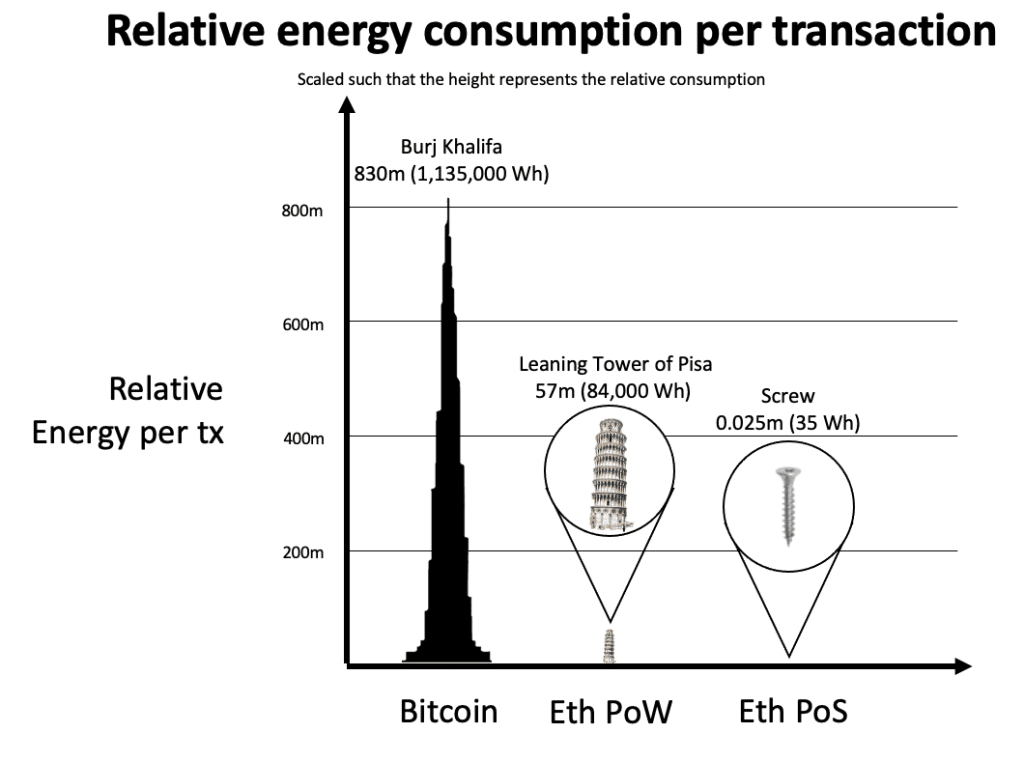
Layer 2 solutions reduce environmental impact by offloading some of the computational work from the main chain. A move from proof-of-work to proof-of-stake, as in Ethereum 2.0can reduce energy consumption by 99.95%.
The introduction of Layer 2 solutions such as State Channels and Rollups further contributes to energy conservation and therefore a more sustainable blockchain ecosystem.
By diverting a majority of transactions from the main network, Layer 2 solutions offer an immediate opportunity to improve environmental efficiency. This significantly reduces the load and energy consumption of the underlying blockchain.
Whether state channels, zero-knowledge rollups or optimistic rollups – all these solutions enable faster transactions without unnecessarily increasing power consumption.
The transition to Layer 2 is not a purely theoretical proposal. Rather, he is in many projects like polygon already a reality.
 Source: Ethereum Foundation Blog
Source: Ethereum Foundation BlogThe merge is a prime example: It is expected to use the power consumption of Ethereum by almost 99.99%, making the chain more environmentally friendly. These initiatives are significant steps towards more sustainable blockchain technologies.
The Green Footprint: How Much CO2 Does Layer 2 Cause?
A data-backed look at emissions from Layer 2 solutions offers some promising numbers:
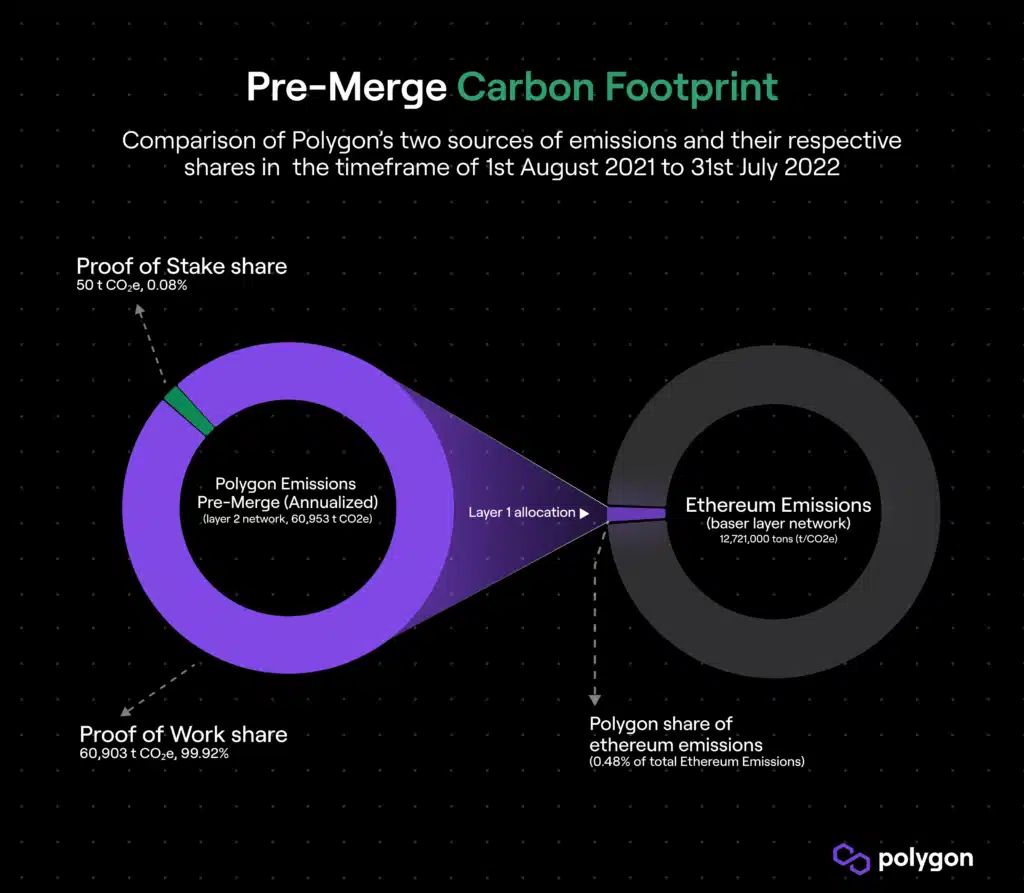
Pre-merge carbon footprint: polygons annual emissions through July 2022 were 60,953.26 tonnes of CO2 equivalent (or tCO2e), with 99.92% from activities on the Ethereum-Base layer originate.
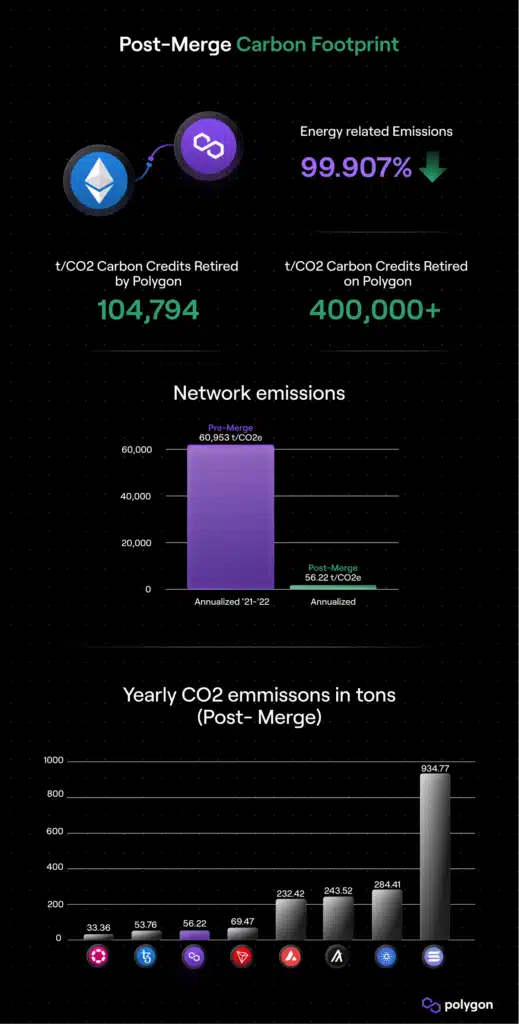
Carbon footprint after the merge: With the merging of Ethereumwhich reduces electricity consumption by 99.99%, reduces CO2 emissions polygon expected to only 56.22 tCO2e annually.
In comparison, PoW consumes of Ethereum as much energy per transaction as a household in 2.8 days, while Layer 2 solutions represent a huge leap towards efficiency and sustainability.
When considering emissions from Layer 2 solutions, the data clearly shows a significant reduction compared to traditional Layer 1 technologies.
Let’s take this for example polygonnetwork, whose annual CO2 emissions by July 2022 were only 60,953.26 tCO2e tons. This number is significantly lower than the output of many Layer 1 networks.
Of these emissions, 99.92% are attributable to the activities of polygon on the Ethereum-Base layer attributed so only 50.13 tCO2e on own PoS network of polygon omitted.
With the expected merge these figures are expected to fall even further, to just 56.22 tCO2e per year.
When compared to global industry or other energy-intensive sectors, the relative impact of Layer 2 solutions is minimal.
This data-driven perspective underscores the critical role Layer 2 technologies play in mitigating blockchain’s environmental impact by aligning with broader sustainability goals and societal demands for cleaner technology solutions.
Conclusion: new visions for a greener crypto future
Layer 2 solutions are not just a theoretical concept, but an important tool to address the pressing environmental challenges posed by blockchain technologies.
By improving scalability, reducing power consumption, and maintaining the core principles of decentralization and security, Layer 2 solutions represent a game-changing step towards sustainable crypto technologies.
Layer 2 environmental impacts are more than just a niche issue. It’s a look into the future of blockchain: a future where technology and sustainability go hand in hand.
For a world grappling with climate change, the adoption and evolution of Layer 2 solutions is not only an exciting technological advance, but also an ethical imperative.
Crypto exchanges with the lowest fees 2023
- Michaël van de Poppe: Bitcoin to Hit $500,000 This Cycle? 🚀💸 Or Just Another Crypto Fairy Tale? - December 21, 2024
- What is the Meme Coin Bonk, Price Predictions 2025–2030, and Why Invest in BONK? - December 18, 2024
- BNB Price Analysis: 17/12/2024 – To the Moon or Stuck on a Layover? - December 17, 2024

















![Best Platforms for Copy Trading in [current_date format=Y] 28 Best Platforms for Copy Trading](https://cryptheory.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/copy-trading-120x86.jpg)





