Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) are a type of digital asset recorded on a blockchain. Compared to utility tokens and cryptocurrencies, NFT tokens have 3 characteristics that set them apart: they are unique, rare, and indivisible.
NFTs can represent many different types of digital assets such as: collectables on blockchain, digital artwork, property in virtual reality, event tickets, gaming items. They can also be used to certify real estate, cars, artwork, and intellectual property of various kinds.
How do NFTs work and their origin
In order to explain to a 5 years old child what NFT tokens are, we could say that they are a bit like figurines on the internet, but with the guarantee of being original and above all unique. And with the possibility of representing everything that has a connotation of scarcity and uniqueness.
In the blockchain world, the information about the identity of an NFT is stored in a smart contract. Each token has its own identity, and therefore an asset cannot be exchanged or replaced with another asset. The data of an NFT saved in a smart contract is like the certificate of authenticity that certain unique artworks possess. While most tokens and cryptocurrencies are fungible, meaning every token is equal to every other token, NFTs are all unique.
There are many who believe that NFTs originated on Ethereum, but this is not the case. The first platform to introduce “blockchain collectables” was Counterparty with the game Spell of Genesis in 2015. Counterparty is a protocol capable of creating digital assets on the Bitcoin blockchain, developed before the arrival of Ethereum.
Spells of Genesis is a tactical fantasy arcade game that cleverly blends strategic aspects of the genre with card collecting and team building. While some cards are already on the blockchain there is an option to “put on the blockchain” the cards created during the game, thus certifying their uniqueness.
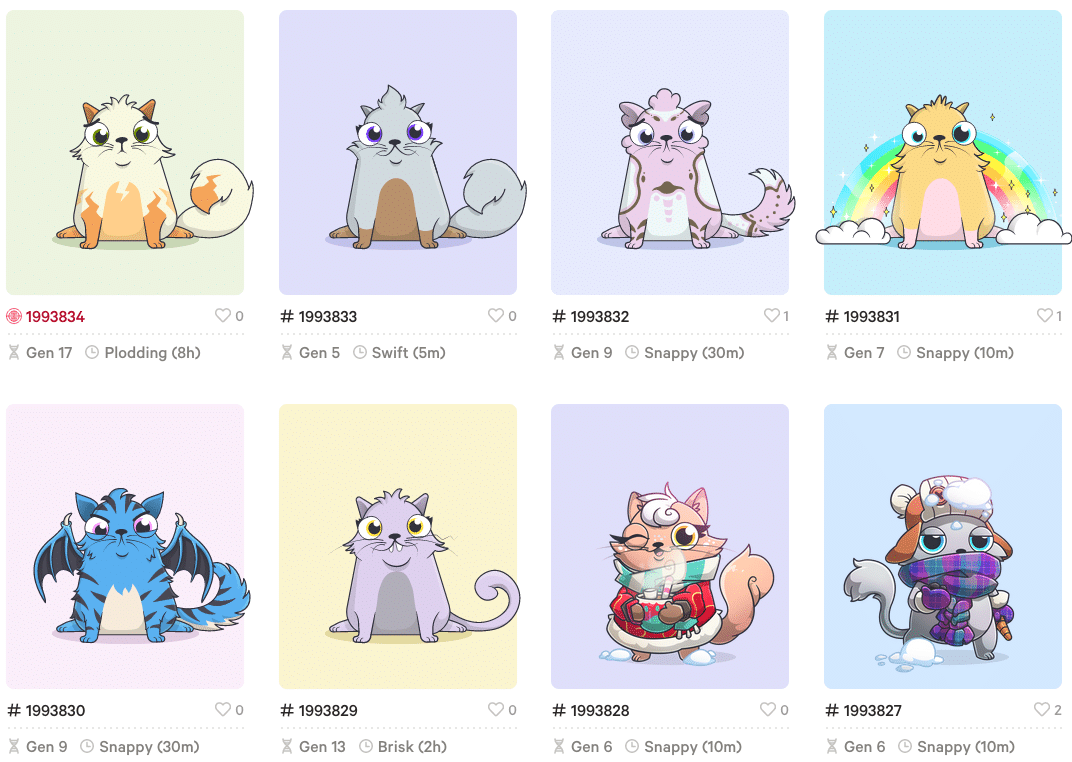
However, the Ethereum ecosystem soon intercepted this market demand and on October 19th, 2017 Dapper Labs launched the famous CryptoKitties game during the Ethereum ETH Waterloo hackathon.
CryptoKitties are collectable digital cats that can be reproduced. When two CryptoKitties breed, the appearance and genetic makeup of their offspring are determined by each parent’s 256-bit genome and an element of luck, leading to 4 billion possible genetic variations.
Kittens are created through “Breeding” and “Siring” (birth). As the kittens are bred they become less and less effective at reproducing, making the rare kittens that can still reproduce extremely valuable. When these kittens become so slow to reproduce that they retire, their offspring will typically take on the title of “most valuable”.
In January 2018, the ERC-721 (Ethereum Request for Comments 721) standard was proposed by William Entriken, Dieter Shirley, Jacob Evans, and Nastassia Sachs. This standard defines a minimum interface that a smart contract must implement to enable the management, ownership and exchange of unique tokens. No standard is imposed for token metadata nor is the addition of additional features restricted, thus leaving full freedom for the artist to insert any kind of content.
Thanks to blockchain technology and smart contracts, the NFT concept introduced for the first time in the history of the internet the specification of uniqueness in the digital world, guaranteed by decentralization and cryptography.
NFT marketplaces
If NFTs are securitized digital certificates, the platforms on which they are traded represent investment banks. These portals perform the work of digitization and registration on blockchain, decide the rules of the markets, and collect their fees when an asset is produced, traded, or optimized.
There are several marketplaces where investors/collectors can trade NFTs. Some deal with almost every category of NFT, while others are dedicated only to specific sectors.
The categories into which the NFT tokens in circulation on these marketplaces fall can be divided into:
- Art
- Collectables
- Gaming
- Metaverse
- Sport
- Utility
According to data from nonfungible.com, the platforms that have generated the most volume so far are Decentraland, an Ethereum-based virtual reality game where you can buy land and build profitable businesses, and CryptoKitties with about 38 million USD generated so far. We then find Axie Infinity, a game based on collectables and SuperRare, a digital artwork marketplace with around 7 million USD.
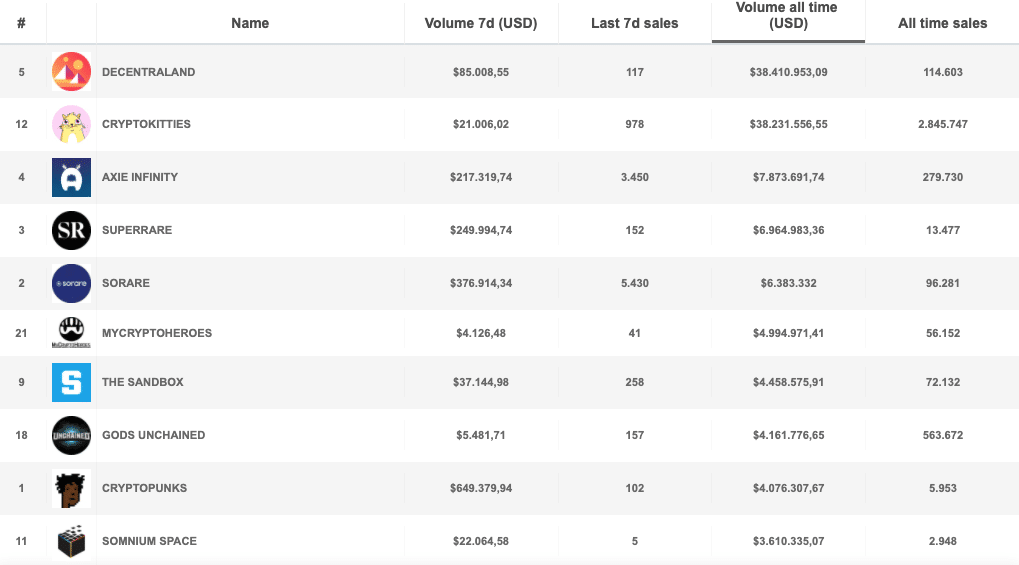
In 5th place is Sorare, a fantasy sports platform that allows you to play a kind of fantasy football on the Ethereum blockchain, with the value of players’ cards linked to the results of real-world football matches.
To get an idea of the interest behind this sector, which has seen steady growth during 2020, the Kylian Mbappé card was sold last month for 116.5 ETH, at today’s exchange rate almost 84,000 USD.
Speaking more broadly, the cumulative market has gradually grown since the end of 2017 at $20 million, reaching the present day with a cumulative value of $150 million. Whereas the average value of NFTs sold has gradually increased to $80.
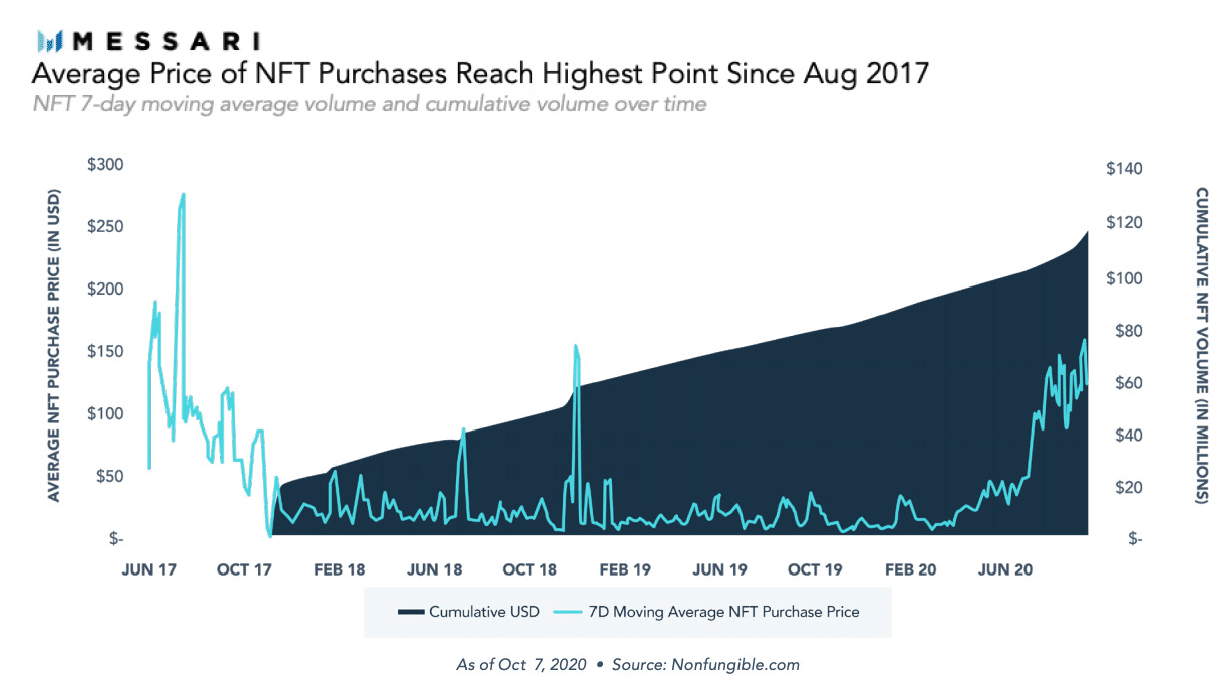
However, NFT markets do not yet have a large number of users, firstly because of the nature of the assets traded which are by definition illiquid since they are scarce, and because the interest of the retail public is still very low.
Besides the virtual reality of metaverses such as Decentraland, CyptoVoxels and Somnium Space, and NFT’s virtual art galleries such as Terra Virtua, it is interesting to note that augmented reality is also present on the blockchain. For instance with Wallem, a game that rewards users with $PTERIA tokens found in the real world around them, with big brand events, where Pteria’s DAO sold PewDiePie’s official NFT for 20 thousand euros on OpenSea. Other important marketplaces are Rarible, SuperRare, CryptoPunks (where an NFT has just been sold for 189.99 ETH, about 137,500 USD) and some platforms built on WAX.
The most popular games, according to nonfungible, are Axie Infinity, Gods Unchained and F1 DeltaTime, an officially licensed Formula 1 game that allows users to buy cars and sections of tracks in the form of NFTs.
Some platforms have experimented with DeFi, such as Rarible’s AXS and Axie Infinity, and liquidity mining programmes have attracted some initial interest.
The future of non-fungible tokens
Many of you will remember that towards the end of 2017, CryptoKitties became so popular that they congested the Ethereum network. The currently most widely used network for NFTs remains Ethereum, but it suffers from the known problems of scalability and network cost. To overcome this problem, some Ethereum sidechains are emerging, such as Matic, Ronin and xDAI. Sorare, the fantasy football platform, is actively participating in Ethereum 2.0 and is also considering SKALE and zk-Rollups.
ETH Killers are also working to grab a slice of the non-fungible token market, and NFTs are appearing on blockchains such as Enjin Network, Flow, WAX, EOS, NEO and Hive. NFT platforms such as Substrapunks and XENO NFT Hub are also coming to Polkadot.
The NFT market and development is facing a future full of surprises. The potential of this sector is still largely unexplored, with possible application to copyright and intellectual property rights, the issuance of tickets and the sale and trade of video games and the representation of gaming objects such as skins.
New areas such as finance and tokenization of real assets are already being explored. A new standard ERC-721o and called ‘Composable Multiclass Fungible Token Standard’ is aimed at derivatives management. With this standard, it will also be possible in future to tokenize portions of property and have a complete picture of their history immediately. The transactions of an NFT will transparently reveal the previous owners.
In short, in a few years’ time, we may find ourselves pervaded by NFTs even if we are not players or collectors on the blockchain: shares, derivatives, works of art, but also certificates of ownership, educational qualifications, licences, guarantees, insurance and everything else imaginable that has its own uniqueness.
The post NFT tokens, the next hype in the blockchain space? appeared first on The Cryptonomist.