A look at on-chain metrics for BTC (BTC) and other cryptocurrencies, specifically the number of new addresses, in order to determine if they support the ongoing price increase.
The number of new addresses supports the price increase in BTC, Compound (COMP) and Aave (AAVE). However, it does not support the increases in Gnosis (GNO) and bZx protocol (BZRX).
BTC (BTC)
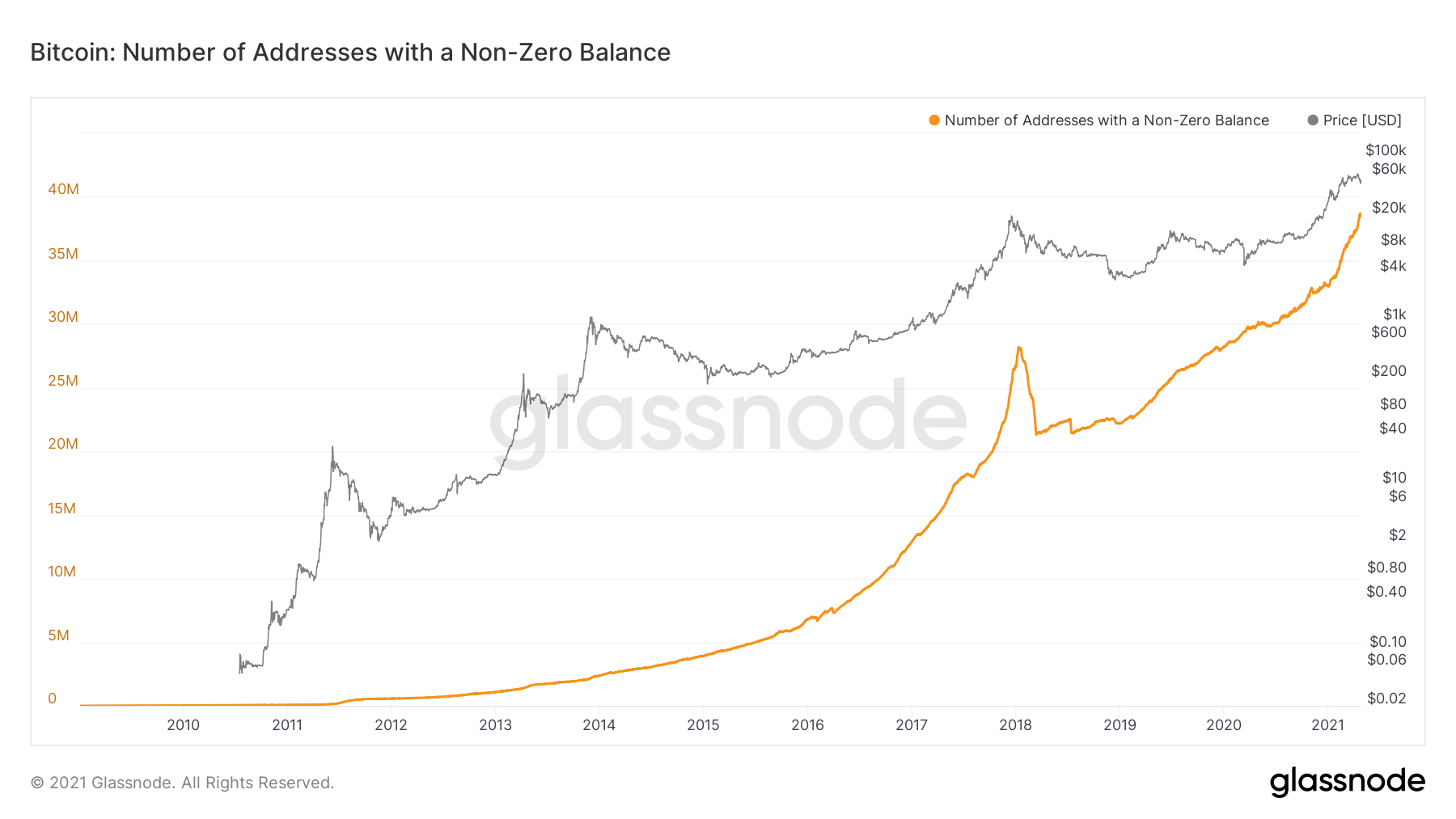
The number of addresses with non-zero balance for BTC has risen steadily since its inception. It began to increase at a faster rate in 2014, right after the high of the cycle was reached.
Afterwards, the rate of increase further accelerated during the bull run of 2016-2017, culminating with a then all-time high of 27,871 million, in January 2018.
The number of addresses decreased considerably during the resulting bear market, most likely due to newer participants liquidating their holdings in an attempt to get out of the market.
In March 2018, three months after the all-time high, the number of addresses was at only 21 million, a roughly 30% reduction from the high.
However, as the new bull market began, the number of addresses also increased as a result, with a new all-time high being reached in November 2018.
As of April 26, there were 38 million new addresses with non-zero balance.
DeFi sector
Compound (COMP)
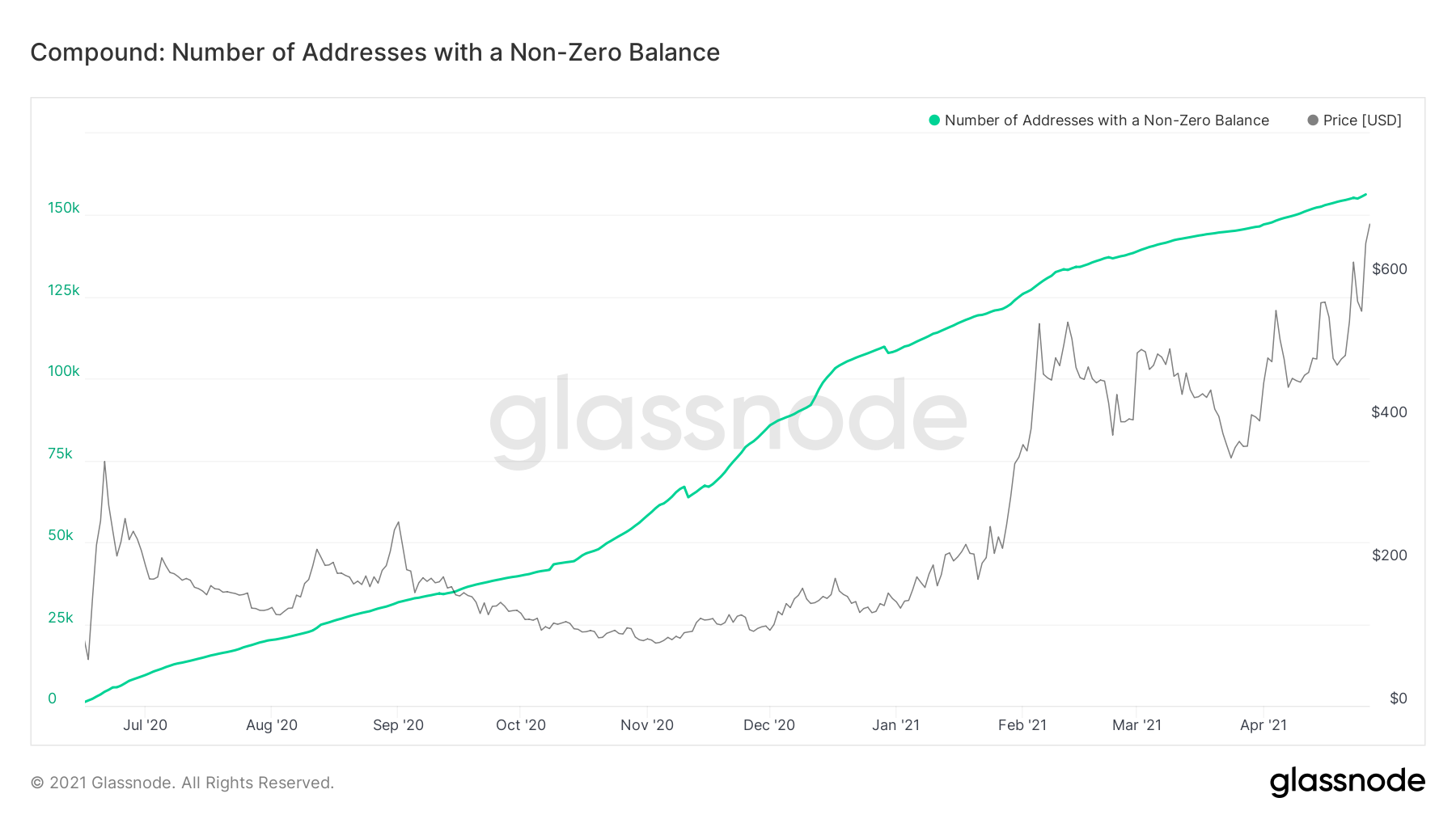
With Compound (COMP) reaching a new all-time high price on April 26, it seems interesting to identify whether this increase is supported by new market participants.
The number of addresses has been steadily rising since September 2020 and has reached all-time highs both during the February 2021 and current all-time high prices.
Therefore, we can state that the price increase is supported by interest in the asset, since new participants are entering the market.
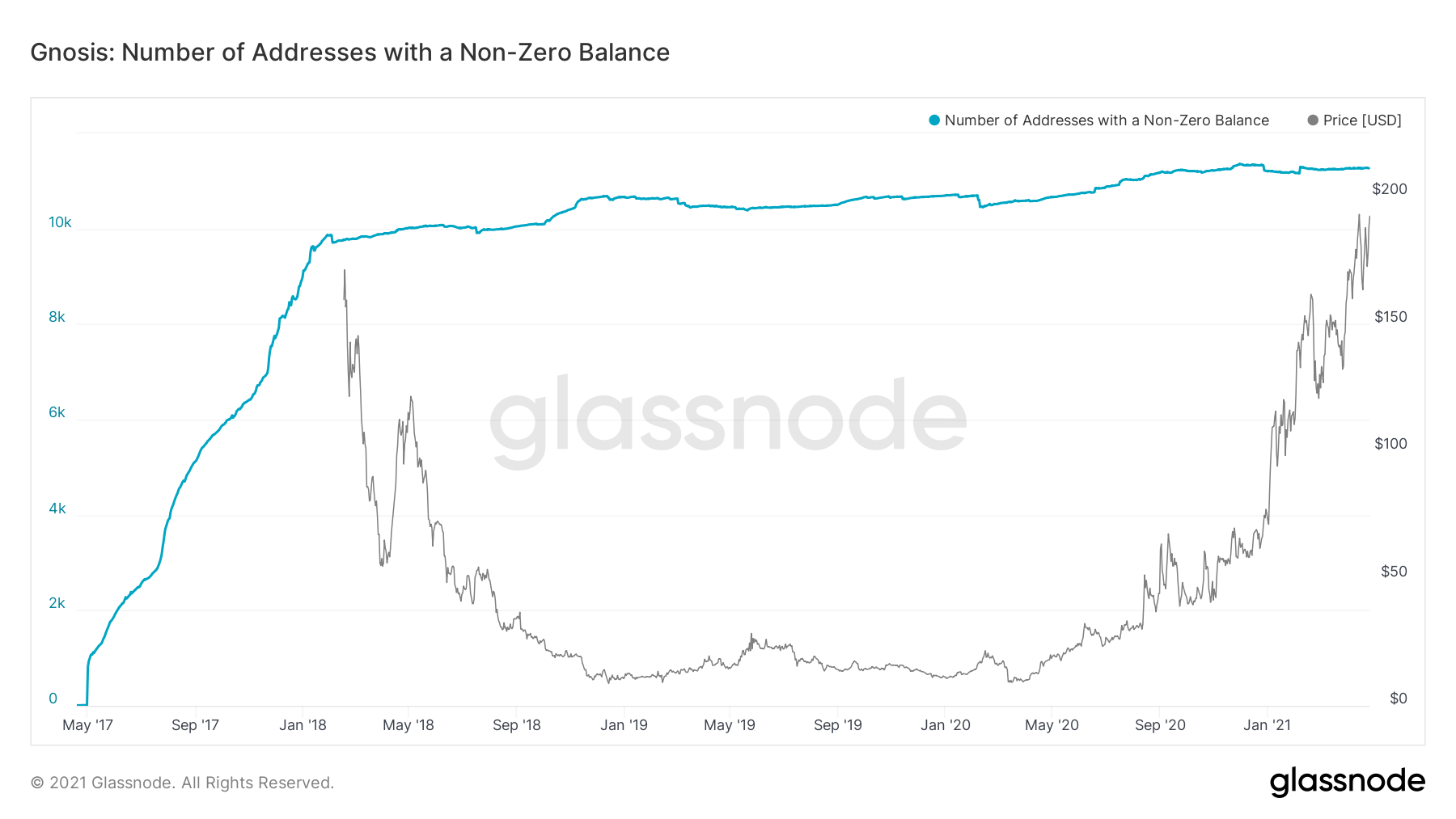
Gnosis (GNO)
However, the same cannot be said about Gnosis (GNO). To the contrary, the number of new addresses has been nearly steady since the 2018 all-time high.
While there were 9,800 new addresses back then, there are 11,200 now, a relatively incremental increase.
In addition, another interesting development is the fact that the number of addresses has been the same regardless of price movements, which is not the case in other altcoins.
Despite a massive price decrease of more than 90% from February to May 2018, the number of addresses stayed the same, meaning that entrants were not liquidating their positions.
However, the number has also been constant during the ongoing increase. This suggests that there are no significant new participants in the market.
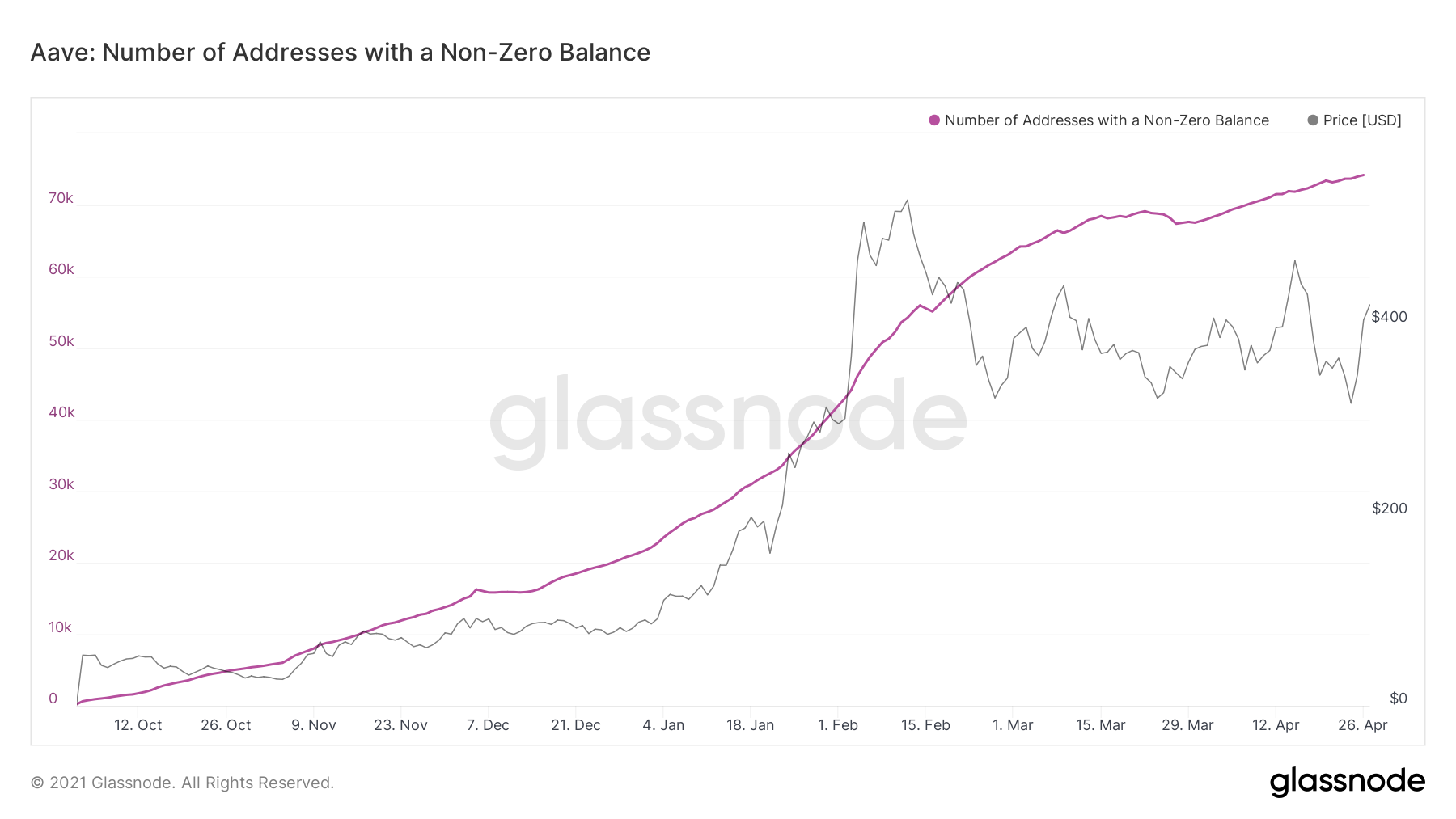
AAVE and BZRX
Two more examples of price increases that are supported and not supported by the number of new addresses are AAVE and BZRX.
The ongoing price increase for AAVE has been accompanied by a steady increase in new market participants.
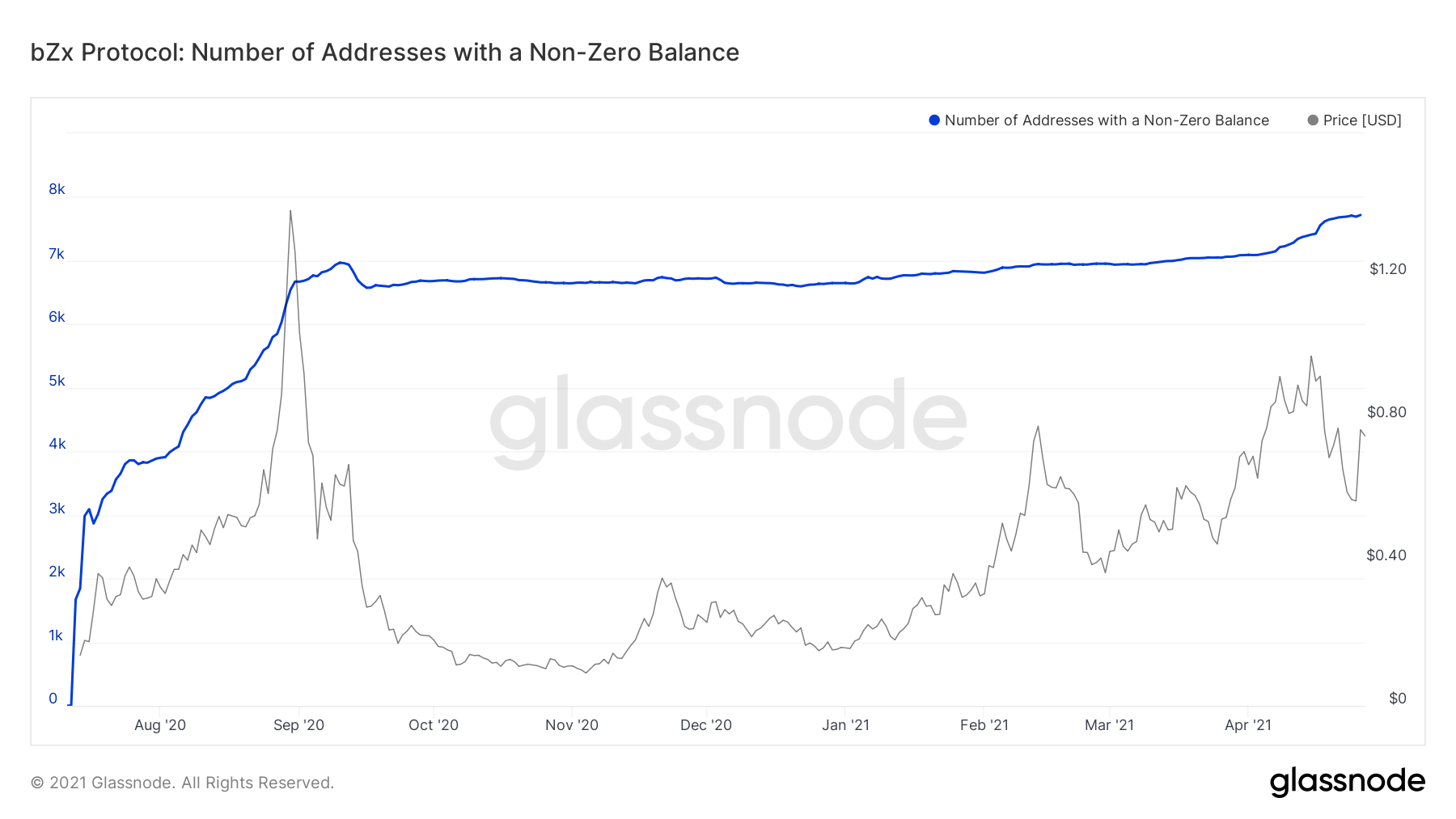
However, the same cannot be said for bZx protocol. Similarly to GNO, the number of new addresses has stayed the same since September 2020.
Conclusion
To conclude, while the number of new addresses supports the increases for BTC, AAVE, and COMP, it does not support the movements of GNO and BZRX.
For BeInCrypto’s latest BTC (BTC) analysis, click here.
The post BTC On-Chain Analysis: Number Of New Addresses Supports Ongoing Price Increase appeared first on BeInCrypto.