The so-called NFTs are revolutionizing the world of online gaming and digital art: one example is Decentraland.
What are NFTs?
NFTs are Non-Fungible Tokens, which are different from classic tokens because, by definition, they are not fungible.
The classic ERC-20 tokens, for example, can be produced in quantities, and all tokens created with a smart contract are the same. In fact, all USDT tokens in ERC-20 format are identical, interchangeable, and have the same value.
However, this does not apply to NFT tokens, which are so different from each other that sometimes they can be absolutely unique.
The most commonly used format is ERC-721, also on the Ethereum blockchain.
The different ERC-721 tokens are not interchangeable with each other, not even if created with the same smart contract, they do not have the same value, but can be freely exchanged by their owners like the ERC-20 tokens.
Therefore, fungible tokens can be replaced or exchanged with any similar token, and this also applies to BTC, or more generically to fiat currencies, such as the US dollar, which is made up of fungible units.
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) on the other hand are not replaceable or exchangeable with other similar tokens, because they are unique pieces, occasionally produced in several identical copies.
In fact, each individual NFT contains information that other NFTs do not have, making it unique. For this reason, they have different values.
At this point, it might be legitimate to wonder what unique and non-fungible tokens are used for.
One of the most obvious applications is to uniquely represent, for example, collectables and to determine their properties.
Since they are exchangeable tokens on the blockchain, each NFT necessarily belongs to one and only one public address, thus establishing its ownership and rarity in an absolute, public and verifiable way by anyone.
Decentraland and NFTs
In the world of online games, non-fungible tokens allow creating unique gaming items that can be freely exchanged among players, bought and sold, or even moved from game to game. This was simply not possible before, given the lack of a global standard such as ERC-721.
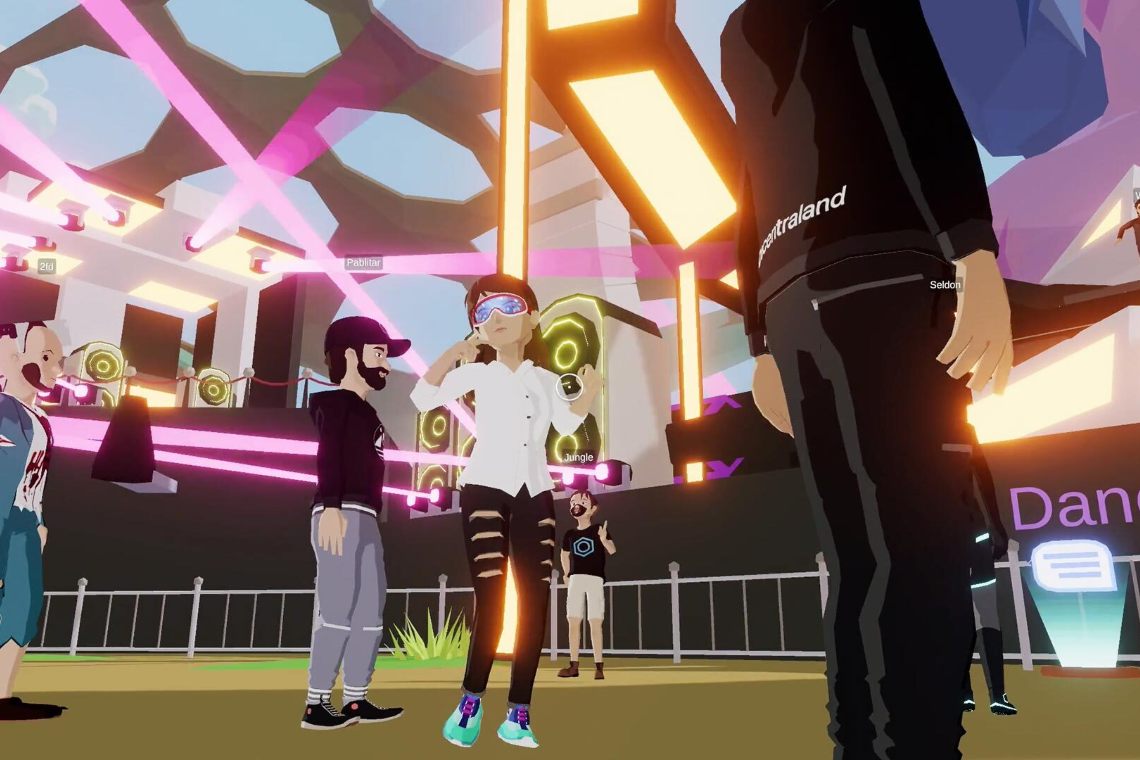
An example in this context is Decentraland, a blockchain-based game that allows buying and selling pieces of land called LAND.
These LAND are NFTs as each land is different from the other in terms of characteristics, design and size.
Decentraland is a very popular game that has recently been gaining ground thanks to a partnership with Binance, but it is just one of many examples of NFT applications in gaming.
These NFTs can also be used to record players’ scores and make them public and transferable from one game to another.
Or they allow the creation of unique entities that are valid and usable across multiple games and platforms.
Another possibility is that they can guarantee rewards to those who own them, depending on how many people use them to play, as in the case of Wallem.
In short, they allow doing things that were simply impossible to do before, if not in an extremely limited and localized way.
They can also be used to uniquely identify a work of art, especially digital art, making it easier for artists to maintain control over their creations and monetize them.
NFTs are still a relatively new technology with a long way to go. Moreover, they are not particularly easy for inexperienced users to use today, and since they use decentralized technology, their scalability is a bit complicated.
However, since they introduce useful new features that have never been possible before, it is very likely that this technology will develop a lot over time.
The post Decentraland and how NFTs are revolutionizing online gaming appeared first on The Cryptonomist.